[STL] 큐 queue
Updated:
큐(queue)란 스택과 같이 데이터를 순서대로 저장하는데 샤용되는 컨테이너형 자료구조를 말합니다. 큐는 LIFO인 스택과 달리 FIFO 구조로 되어있습니다.
FIFO$($First In First Out) : 한쪽 끝 $($rear)에서 삽입이 일어나고 다른 끝 $($front)에서 삭제가 일어나는 리스트
- front : 맨 마지막으로 삭제된 데이터의 인덱스를 가리키는 포인터.
- rear : 맨 마지막에 삽입된 데이터의 인덱스를 가리키는 포인터.
단순 큐의 선언 및 삽입과 삭제
일차원 배열 queue[capacity]를 동적 할당하여 선언하고 초기의 front=rear=-1, 큐가 full인 경우 : rear=capacity-1큐가 empty인 경우 : front==rear로 선언합니다.
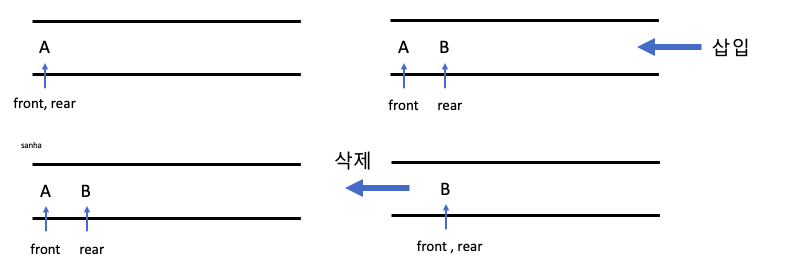
단 이러한 조건으로 삽입, 삭제가 반복될 경우 삭제로 인해 생긴 공간이 있음에도 rear==capacity-1 조건을 만족시켜 queue가 full로 나타나는 상황이 발생하게 됩니다. 이러한 문제점을 해결하기 위해 원형 큐를 이용하여 큐를 구현할 수 있습니다.
[ADT] 원형 큐의 구현
일차원 배열을 원형으로 간주합니다.
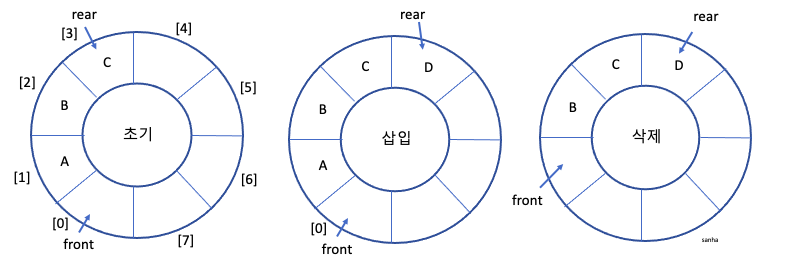
배열의 맨 마지막 인덱스 다음을 index[0]으로 봅니다.
index : 0->1->2->3->4->5->6->7->0->1->2…
따라서 원형 큐에서 front와 rear의 이동은 rear=(rear+1)%capacity, front=(front+1)%capacity으로 처리하여야 인덱스가 원형으로 돌아갈수 있습니다.
+
if(rear==capacity-1) rear=0;
else rear++;
// 위의 if문은 rear = (rear+1)%capacity와 같음
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Queue
{
private:
int *queue;
int front;
int rear;
int capacity;
public:
Queue();
void Push(int &x);
void Pop();
void showSize();
bool isEmpty();
void showFront();
void showBack();
};
Queue::Queue(int queueCapacity=1)
{
capacity=queueCapacity;
queue=new int[capacity];
front=rear=0;
}
void Queue::Push(int &x)
{
if((rear+1)%capacity==front) //큐가 full인지 확인
{//큐가 full이면 크기를 두 배로 늘려준다.
capacity*=2;
int *temp = new int[capacity];
for(int i=0; i<=rear; i++)
temp[i]=queue[i];
queue=temp;
delete []temp;
}
rear=(rear+1)%capacity; //큐가 full이 아닌 경우
queue[rear]=x;
}
void Queue::Pop() //FIFO
{
if(front==rear) cout<<"-1\n";
else front=(front+1)%capacity;
}
void Queue::showSize()
{
cout<<rear-front<<'\n';
}
bool Queue::isEmpty()
{
if(front==rear) return true;
else return false;
}
void Queue::showFront()
{
if(front==rear) cout<<"-1\n";
else cout<<queue[front]<<'\n';
}
void Queue::showBack()
{
if(front==rear) cout<<"-1\n";
else cout<<queue[rear]<<'\n';
}
[STL] 큐의 멤버함수 및 사용
#include<queue> //큐가 있는 헤더파일
queue<Data_type> q
- push$($element) : 큐의 끝에 원소 삽입
- pop$($) : 큐의 첫번째 원소 삭제
- size$($) : 큐에 있는 원소의 개수 반환
- empty$($) : 큐가 비었으면 true 아니면 false를 반환
- front$($) : 큐의 가장 첫번째 원소 반환
- back$($) : 큐의 가장 마지막 원소 반환
예제
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(1);
q.push(2);
q.push(3);
// q[1 2 3]
cout<<"큐의 크기 : "<<q.size()<<'\n'; //3
cout<<"큐의 첫번째 원소값 : "<<q.front()<<'\n';
cout<<"큐의 맨 마지막 원소값 : "<<q.back()<<'\n';
q.pop(); // 1 삭제
// q[2 3]
cout<<"큐의 첫번째 원소값 : "<<q.front()<<'\n'; //2
cout<<"큐의 맨 마지막 원소값 : "<<q.back()<<'\n';
q.pop(); // 2 삭제
q.pop(); // 3 삭제
if(q.empty()) cout<<"큐가 비었다";
return 0;
}
결과
큐의 크기 : 3
큐의 첫번째 원소값 : 1
큐의 맨 마지막 원소값 : 3
큐의 첫번째 원소값 : 2
큐의 맨 마지막 원소값 : 3
큐가 비었다
Leave a comment